Solar Battery Systems for Homes: Power Your Future with Energy Independence
Explore everything you need to know about solar battery systems for homes—from how they work to how to choose the right one for your needs.
As the world continues to grapple with climate change and energy instability, more homeowners are seeking cleaner, more sustainable ways to power their homes. One of the most impactful solutions available today is a solar battery system for home use. These systems not only help reduce electricity bills but also provide energy independence and backup power during outages. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about solar battery systems for homes—from how they work to how to choose the right one for your needs.
What Is a Solar Battery System for Home Use?
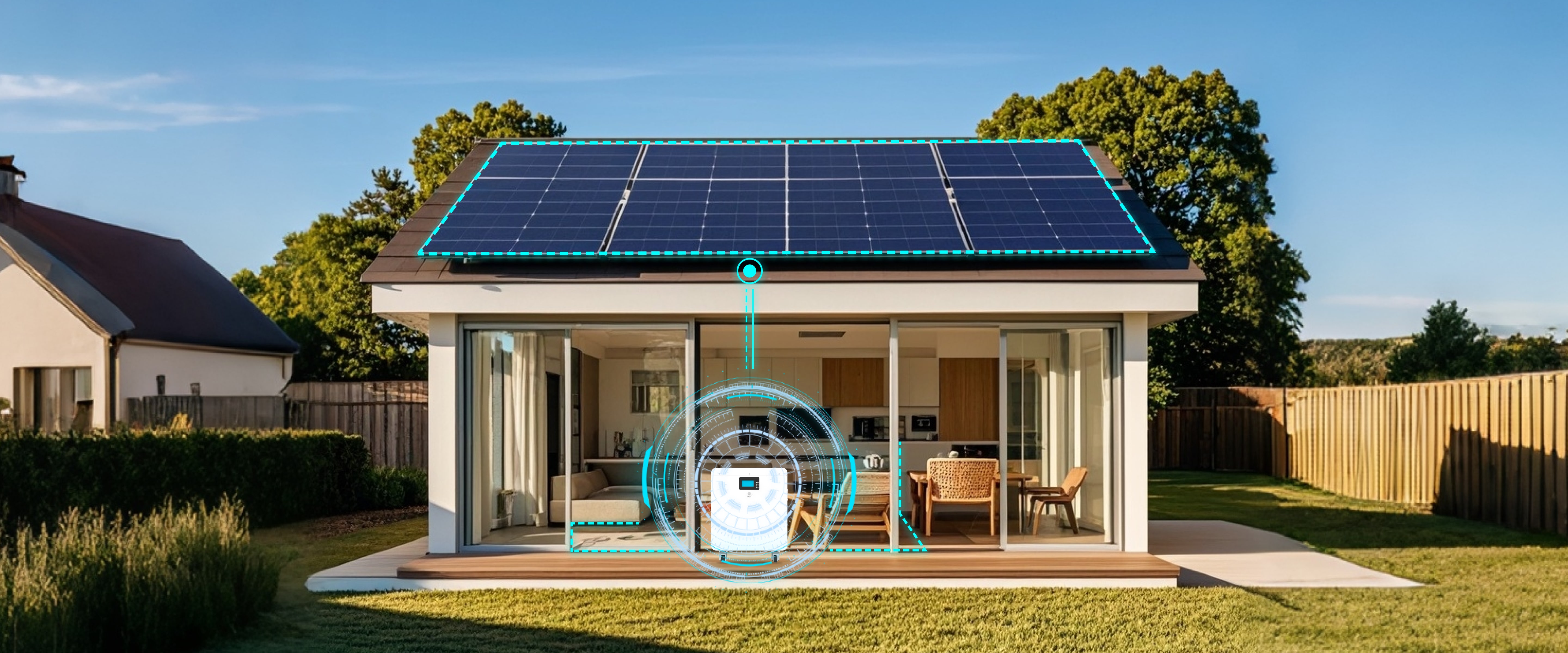
A solar battery system for home use is a setup that stores energy generated by solar panels during the day and makes it available for use during the night or during a power outage. These systems consist primarily of one or more batteries connected to a solar photovoltaic (PV) system. Instead of sending excess solar electricity back to the grid, the system stores it for later use.
This stored energy can be used to power appliances, lighting, and even heating or cooling systems when sunlight is unavailable. Solar battery systems offer an important layer of reliability and are an excellent investment for those who live in areas prone to blackouts or high utility rates.
In essence, solar battery systems for homes give homeowners more control over their energy usage and expenses while helping them contribute to a cleaner environment.

How Solar Battery Systems Work
The operation of a solar battery system for home use is a coordinated effort between several key components. Here's a simplified breakdown of how the system works:
- Solar Panels Collect Sunlight: During the daytime, solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter Converts Energy: An inverter converts the DC electricity to alternating current (AC), which is suitable for use in your home.
- Powering the Home: The AC electricity is then used to run household appliances.
- Storing Excess Energy: If your system produces more electricity than needed, the excess is stored in the battery system rather than being sent to the grid.
- Drawing from the Battery: At night or during power outages, your home draws electricity from the battery storage instead of the grid, keeping the lights on and essential systems running.
- Grid Backup: If your battery runs out of power and you are connected to the utility grid, the grid can serve as a final backup source of electricity.
Some advanced systems can be configured to sell unused electricity back to the utility provider through net metering programs, offering further economic benefits.
Why Homeowners Are Choosing Solar Battery Systems
The growing popularity of solar battery systems for homes is driven by a combination of economic, environmental, and practical factors:
- Energy Independence: By storing your own solar energy, you reduce reliance on the grid and gain greater control over your electricity.
- Emergency Backup: These systems provide backup power during outages, which is especially important in areas affected by storms, wildfires, or utility disruptions.
- Electricity Bill Savings: Stored solar energy can be used during peak rate periods when electricity from the grid is most expensive, reducing your energy bills significantly.
- Environmental Sustainability: Utilizing solar energy reduces your carbon footprint and contributes to global efforts to combat climate change.
- Home Value Increase: Homes with solar battery systems are often more attractive to buyers, potentially increasing property value.
Types of Solar Battery Technologies
There are several battery types used in solar battery systems for homes, each with distinct characteristics and suitability:
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Pros: High energy density, lightweight, long lifespan (10–15 years), low maintenance
Cons: Higher upfront cost
Best For: Homeowners looking for efficiency, compactness, and long-term performance
2. Lead-Acid Batteries
Pros: Lower initial cost, well-established technology
Cons: Shorter lifespan (5–10 years), bulkier, requires regular maintenance
Best For: Budget-conscious installations and off-grid applications
3. Flow Batteries
Pros: Long cycle life, scalable, low degradation
Cons: High cost, more complex setup
Best For: Large-scale residential or commercial applications with long-term goals
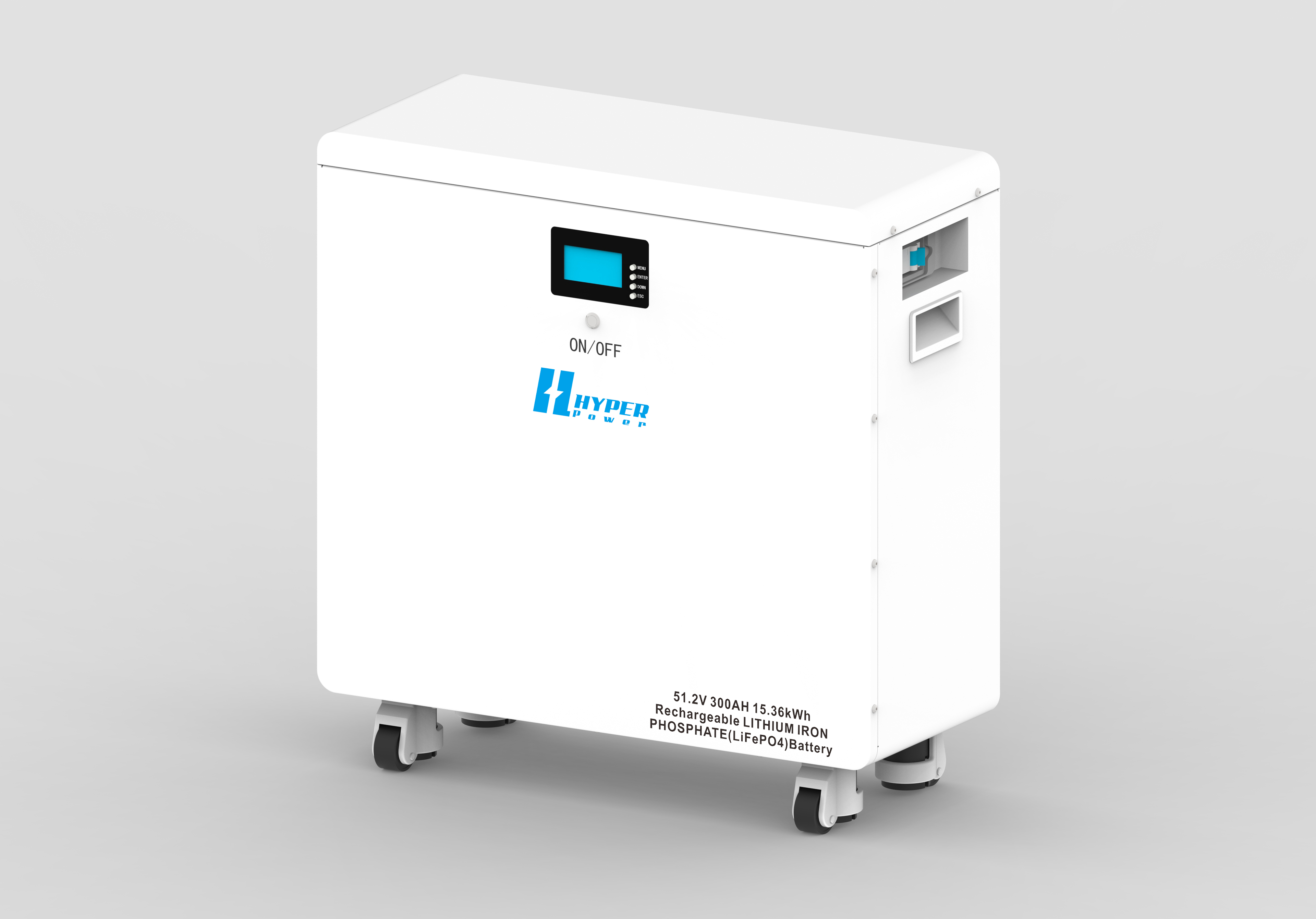
Key Components of a Home Solar Battery System
A functioning solar battery system for home use involves multiple components working together:
Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and generate DC electricity.
Inverter: Converts DC to AC for home use.
Battery Storage Unit: Stores excess electricity for later use.
Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of electricity into and out of the battery.
Battery Management System (BMS): Protects the battery from overcharging or deep discharging.
Monitoring System: Allows homeowners to track energy production, usage, and battery status through a mobile app or web interface.
How to Size a Solar Battery System for Your Home
Proper sizing of your solar battery system for home ensures you have sufficient power without overspending. Consider the following steps:
- Calculate Daily Energy Usage: Check your electricity bill to find average daily kWh consumption.
- Determine Backup Needs: Decide how many hours or days of backup you want.
- Factor in Battery Specs: Consider Depth of Discharge (DoD) and efficiency ratings.
- Match System Size: Choose a battery capacity that meets or exceeds your backup goals, allowing a buffer for inefficiency.
Example:
- If your home consumes 30 kWh daily and you want 24-hour backup, a system with at least 35–40 kWh capacity is advisable.

Return on Investment (ROI) and Savings
A well-designed solar battery system for home use can offer substantial long-term savings:
- Lower Monthly Bills: Use stored solar energy during peak rates.
- Tax Incentives: The U.S. federal tax credit can offset 30% of the system cost.
- Avoided Outage Costs: Prevent food spoilage, HVAC disruptions, and loss of productivity during blackouts.
Estimated ROI:
Most homeowners see a return within 7 to 10 years, with lifetime savings potentially exceeding $20,000 depending on local electricity rates and usage patterns.
Installation Process and What to Expect
Installing a solar battery system for home use involves several steps:
Home Assessment: Evaluate roof space, sunlight exposure, and electrical setup.
System Design: Tailor the system to meet your household needs.
Permit Approval: Submit designs to local authorities.
System Installation: Typically completed within 1–3 days.
System Inspection and Activation: Ensure everything meets safety and electrical codes.
Conclusion
Investing in a solar battery system for home use is one of the smartest decisions a homeowner can make in today’s energy landscape. Not only do solar battery systems for homes provide financial and environmental benefits, but they also give you peace of mind in uncertain times.
From reducing reliance on the grid to ensuring power during outages and lowering electricity bills, these systems are redefining modern home energy solutions. With the right setup, homeowners can unlock decades of clean, reliable, and cost-effective power.
Whether you're preparing for outages, saving money, or simply going green, there's never been a better time to embrace solar battery storage at home.
Blog

Maximizing Energy Independence with Home Lithium Battery Storage

How Residential Photovoltaic Energy Storage Systems Empower Sustainable Homes

Why the 12V Lithium Ion Car Battery is the Smarter Automotive Power Solution — Insights from JEJE Energy









-Charging.png)
.jpg)