The Ultimate Guide to Lithium-Ion Home Batteries: Backup Power Solutions for Modern Homes
Explore everything you need to know about lithium-ion home batteries, from their working principles and benefits to their installation, maintenance, and future prospects.
In an era where power outages are increasingly common and energy costs continue to rise, homeowners are turning to lithium-ion home batteries as a reliable backup power solution. These advanced energy storage systems not only provide backup power during blackouts but also contribute to overall energy efficiency and cost savings. Furthermore, as the demand for renewable energy systems like solar power increases, lithium-ion batteries are becoming integral components for energy storage and load management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about lithium-ion home batteries, from their working principles and benefits to their installation, maintenance, and future prospects.
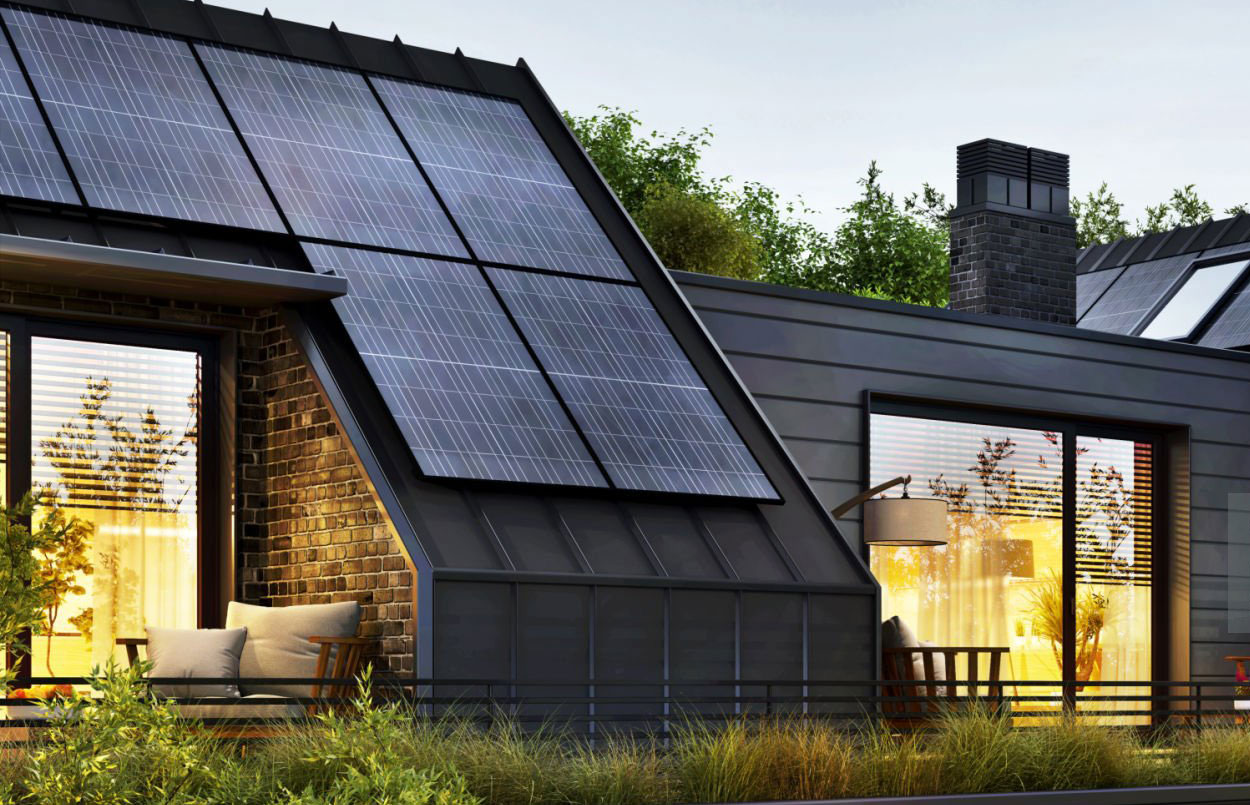

Understanding Lithium-Ion Home Batteries
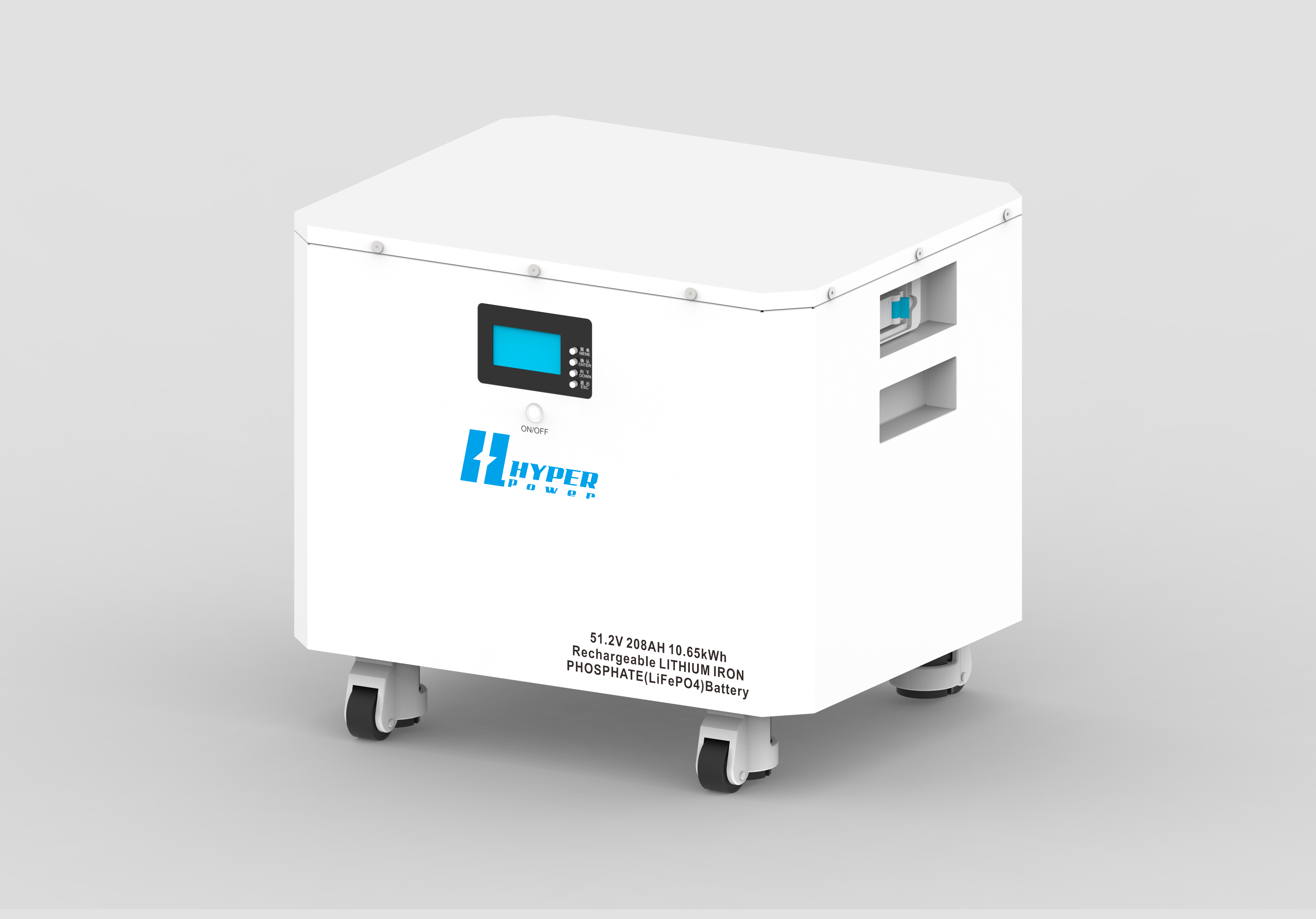
Lithium-ion home batteries are energy storage devices that utilize lithium-ion cells to store and discharge electrical energy. Unlike traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, faster charging times, and a longer lifespan. These characteristics make them ideal for residential applications where space, efficiency, and performance are critical considerations. Additionally, lithium-ion home batteries are known for their lightweight design and relatively low maintenance requirements, making them a popular choice for modern, tech-savvy households.
How Do Lithium-Ion Home Batteries Work?
Lithium-ion home batteries operate based on the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. When the battery is being charged, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through an electrolyte solution. During discharge, the ions travel back to the cathode, generating a flow of electricity that can power household appliances and systems. This reversible chemical reaction enables multiple charge and discharge cycles without significant degradation, allowing lithium-ion batteries to maintain their capacity and performance over many years. The use of advanced battery management systems (BMS) further optimizes the charging and discharging process, ensuring the battery operates safely and efficiently.
Applications of Lithium-Ion Home Batteries
Backup Power: Lithium-ion home battery backup systems provide emergency power during grid outages, ensuring uninterrupted operation of critical appliances such as refrigerators, medical equipment, and communication devices. For instance, during severe weather conditions, these batteries can supply power for several hours, preventing food spoilage and maintaining connectivity.
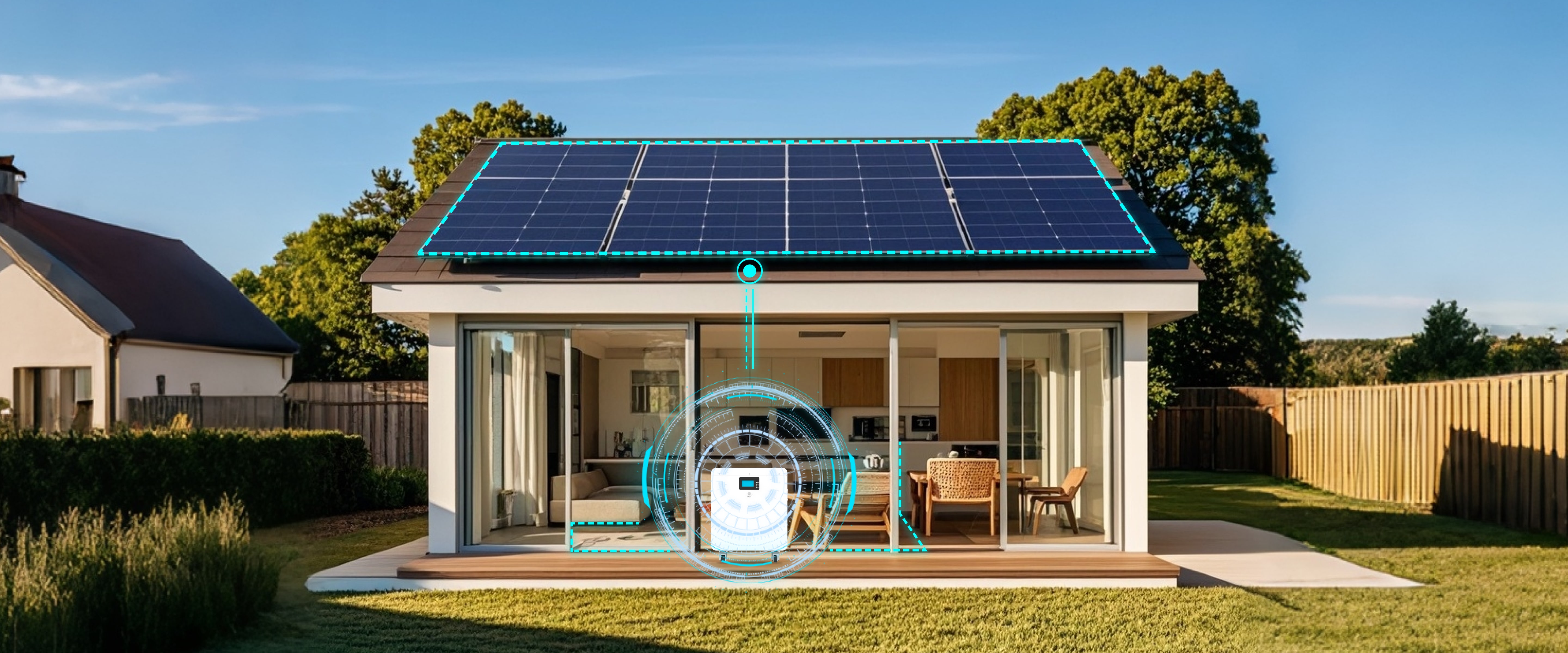
Energy Storage for Solar Systems: Homeowners with solar panels can use lithium-ion batteries to store excess solar energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days, maximizing the utility of their solar installations. This stored energy can be particularly valuable during peak demand periods when electricity rates are higher.
Peak Shaving and Load Management: Lithium-ion batteries can store energy during off-peak hours and release it during peak demand periods, reducing electricity costs and easing grid strain. This strategy not only saves money but also contributes to grid stability by reducing the overall load during peak hours.
Key Benefits of Lithium-Ion Home Battery Backup Systems
High Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries store more energy in a smaller footprint compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them suitable for residential installations with limited space.
Longer Lifespan: They typically last 10-15 years, with thousands of charge cycles, making them a cost-effective investment over the long term. Furthermore, technological advancements have improved the durability and safety of lithium-ion batteries, reducing the risk of thermal runaway and other safety hazards.
Fast Charging: Lithium-ion batteries can recharge rapidly, minimizing downtime during outages. This fast-charging capability is especially beneficial for homeowners who rely on solar power, as it enables them to quickly store energy during optimal solar hours.
Scalability: Homeowners can add more battery modules as needed to expand storage capacity, allowing for customization based on energy needs. This modular approach is ideal for growing households or those planning to increase solar capacity in the future.
Environmental Impact: Lithium-ion batteries are more environmentally friendly than lead-acid batteries, as they contain fewer toxic materials and are more recyclable. Additionally, they contribute to the broader adoption of renewable energy systems by enabling efficient energy storage and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Considerations: Proper placement, inverter compatibility, and electrical panel configuration are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Homeowners should work with certified installers to ensure compliance with local building codes and safety regulations.
Maintenance Tips: Periodic inspection, software updates, and monitoring battery health are essential for maximizing lifespan and performance. Most modern systems come with built-in diagnostic tools that provide real-time monitoring and alerts.
Safety Precautions: Ensuring adequate ventilation, preventing overheating, and managing battery disposal responsibly are critical for maintaining safe operation. Lithium-ion batteries should be installed away from flammable materials and in areas with sufficient airflow.
Costs and Incentives
Initial Investment: Typical costs range from $5,000 to $15,000 depending on capacity, brand, and installation requirements. While the upfront cost can be substantial, the long-term savings in reduced energy bills and potential revenue from grid services can offset the initial investment.
Incentive Programs: Federal and state tax credits, rebates, and net metering options can significantly reduce the overall cost of lithium-ion home battery systems. Programs such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and state-specific incentives provide financial relief for homeowners investing in energy storage.
Long-Term Savings: Reduced energy bills, minimized grid reliance, and potential income from energy resale can make lithium-ion home batteries a financially viable investment. Additionally, time-of-use pricing structures can further enhance savings by enabling homeowners to use stored energy during peak rate periods.

Future Trends in Lithium-Ion Home Batteries
Advanced Battery Chemistries: Innovations in solid-state and lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are expected to improve safety, energy density, and cost-efficiency.
Integration with Smart Home Systems: Enhanced monitoring, AI-driven energy management, and remote control via mobile apps are shaping the future of home energy systems, allowing homeowners to optimize power usage and reduce costs.
Grid Services and Virtual Power Plants: Home batteries as grid support assets, enabling demand response, grid balancing, and participation in virtual power plant programs that pay homeowners for excess energy stored in their batteries.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion home batteries are transforming residential energy storage by providing reliable backup power, optimizing solar energy usage, and reducing dependence on the grid. As technology continues to advance, these systems will become even more efficient, affordable, and seamlessly integrated into smart home ecosystems. Whether you're looking to safeguard against power outages or reduce your energy bills, investing in a lithium-ion home battery can be a game-changing decision for a more sustainable and resilient home.
Blog

Maximizing Energy Independence with Home Lithium Battery Storage

How Residential Photovoltaic Energy Storage Systems Empower Sustainable Homes

Why the 12V Lithium Ion Car Battery is the Smarter Automotive Power Solution — Insights from JEJE Energy
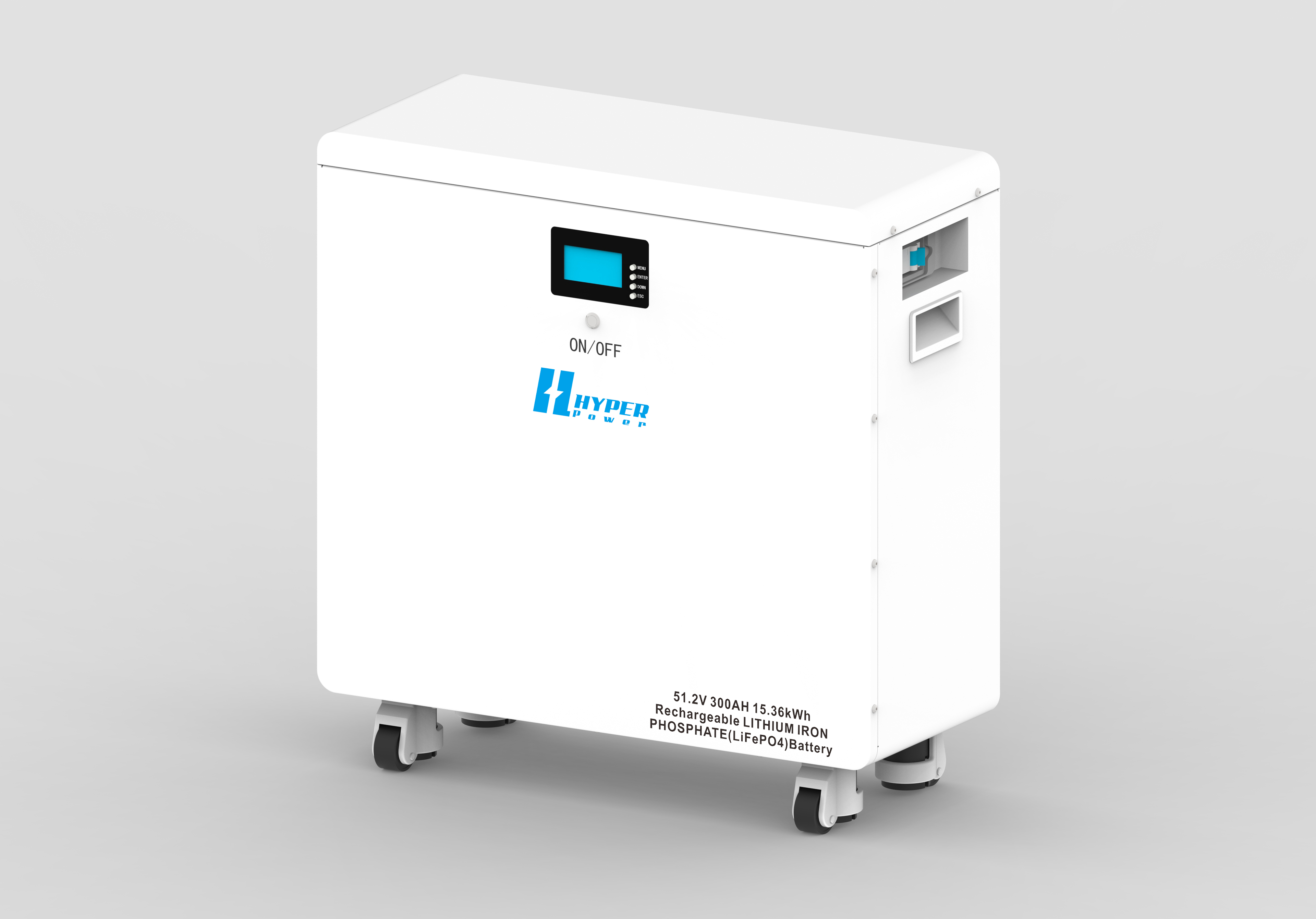








-Charging.png)
.jpg)